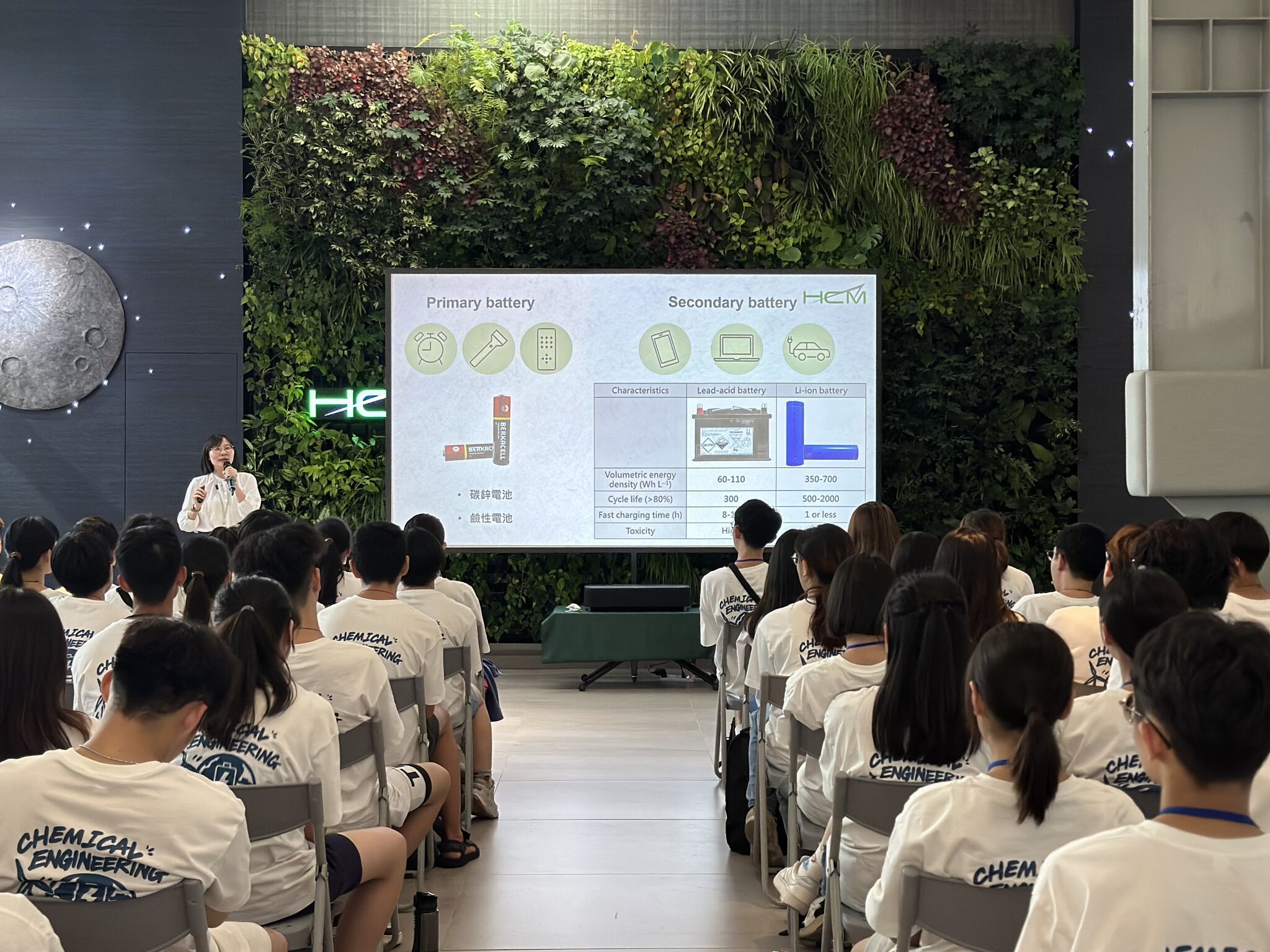
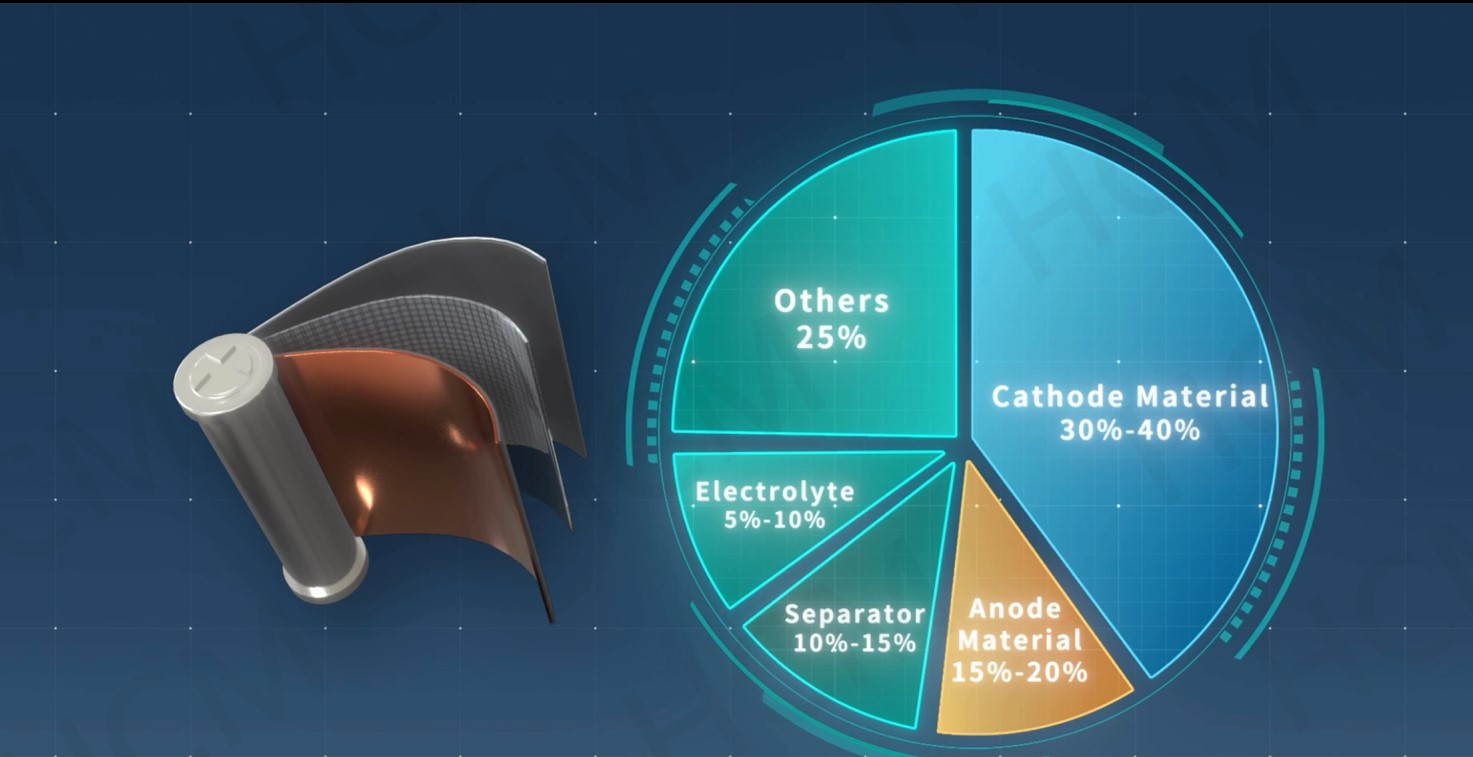
Material Comparison: LFP vs LMFP ⚡🔋
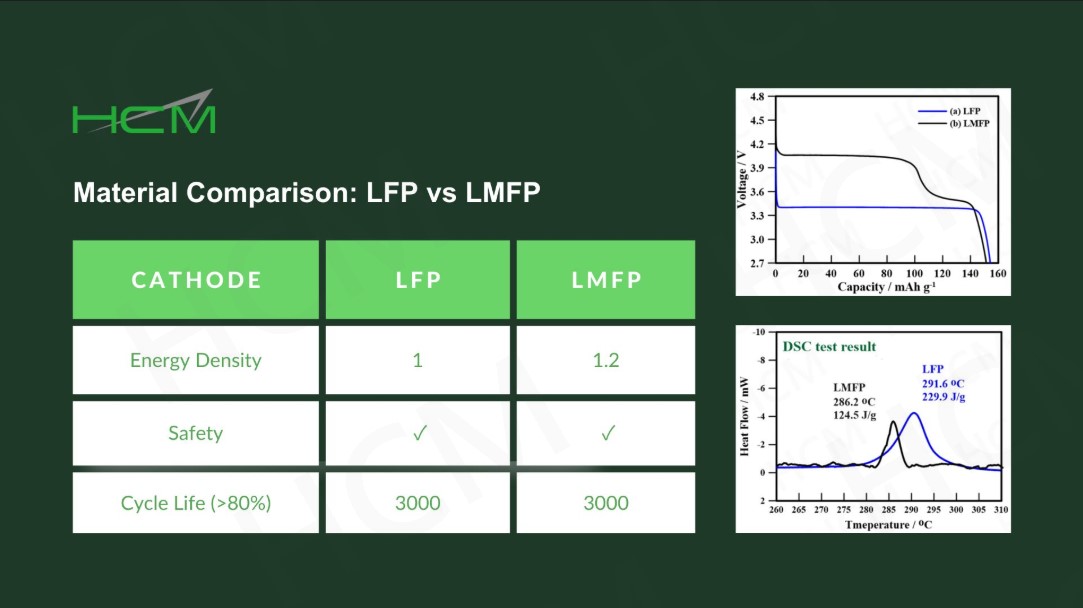
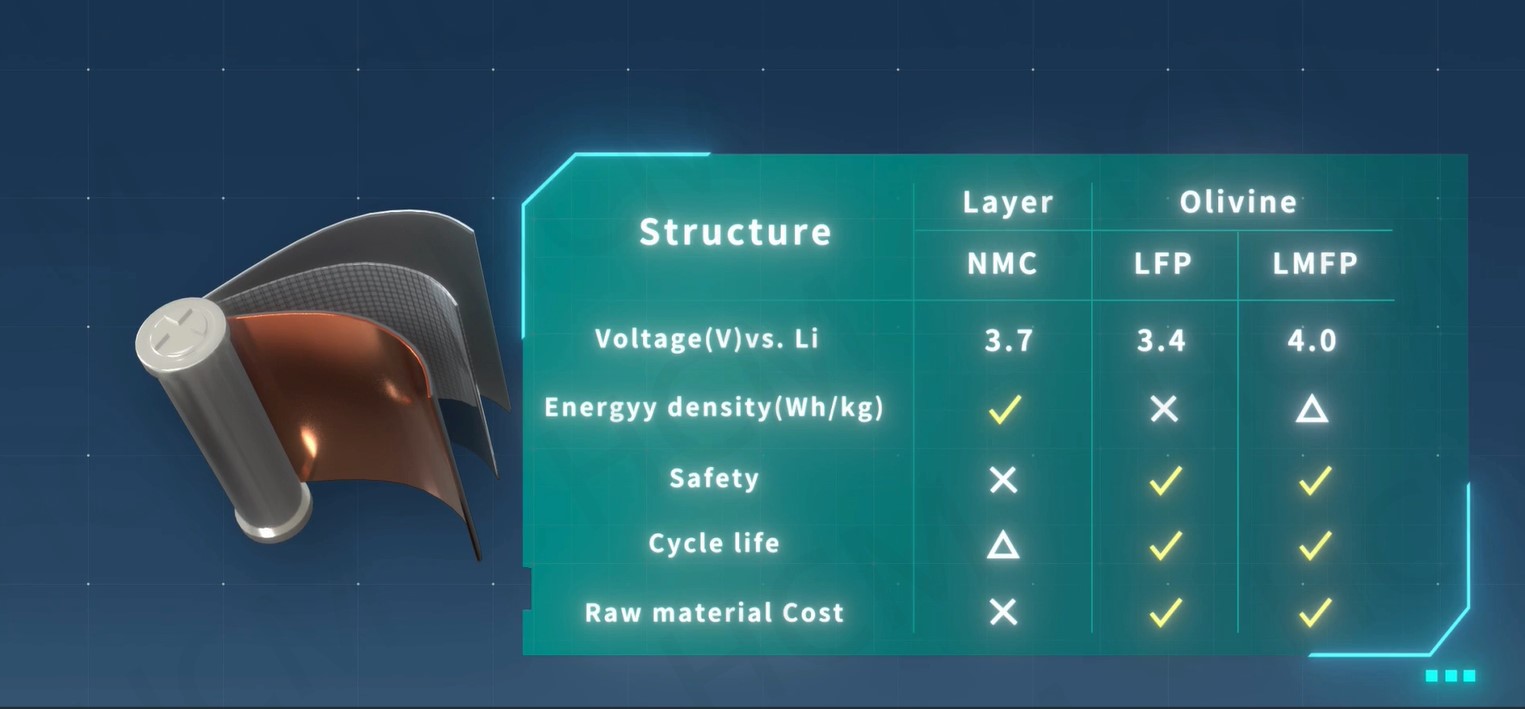
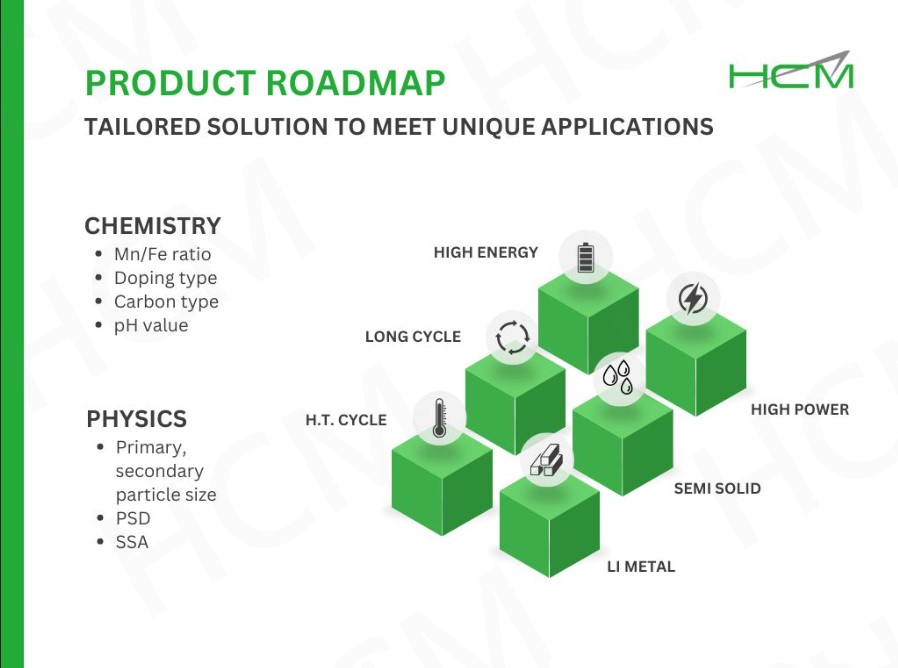
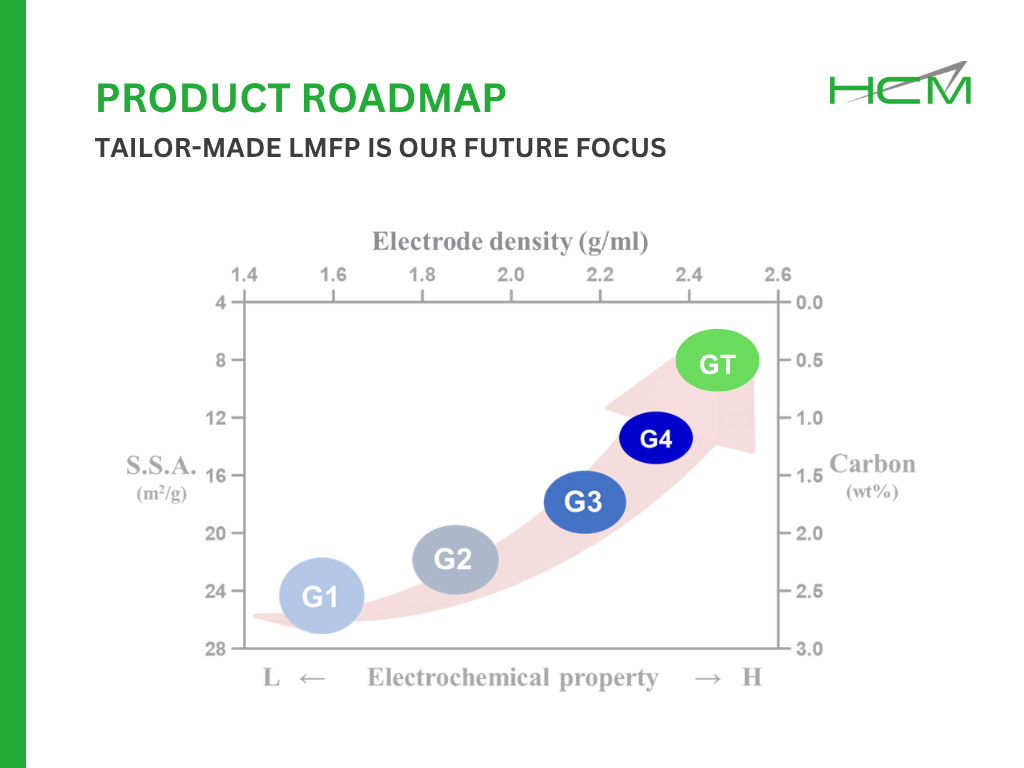
As battery technology advances, Lithium Manganese Iron Phosphate (LMFP) is emerging as a strong alternative to Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP). While both share the safe and stable olivine structure, LMFP offers key advantages:
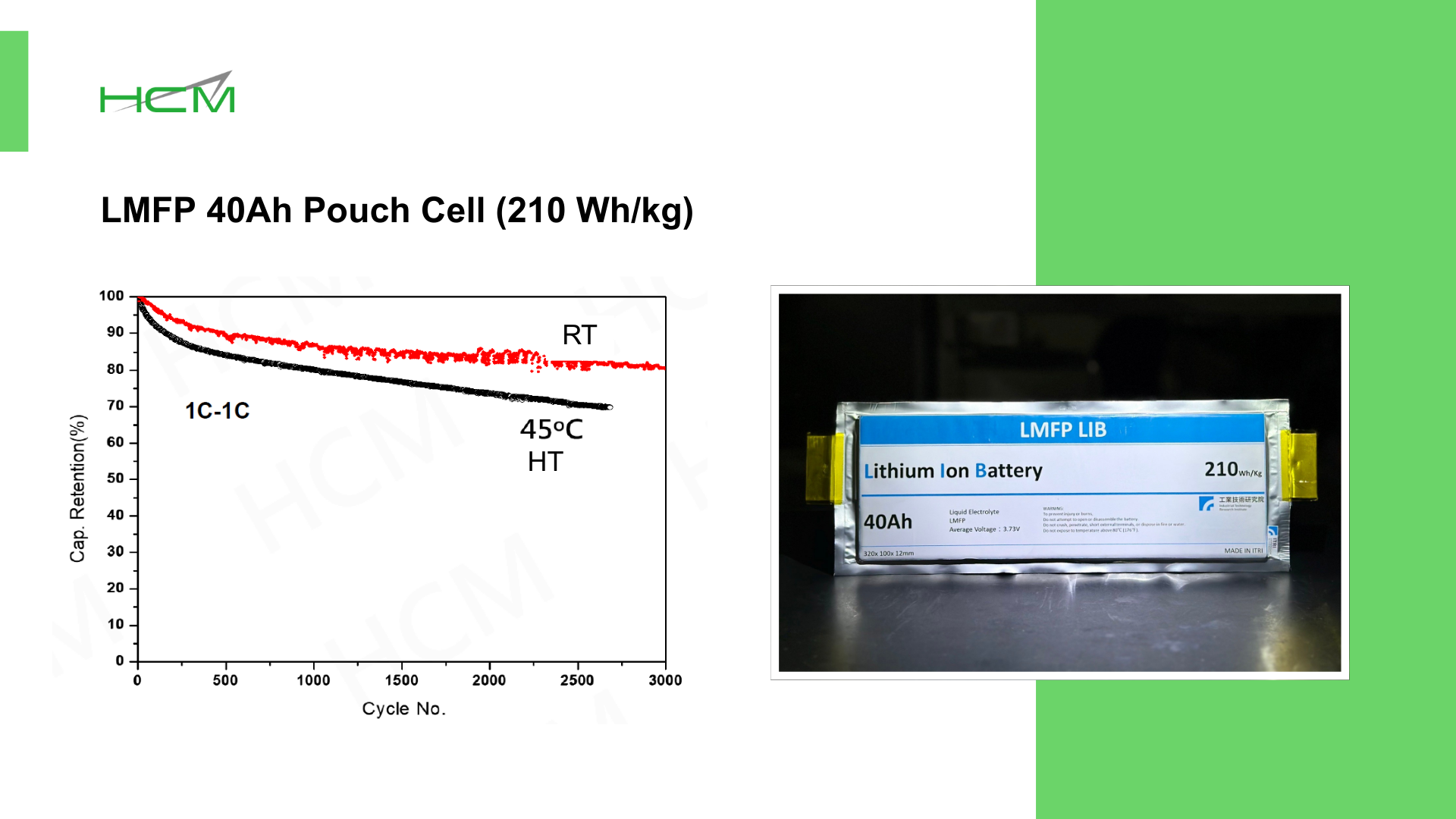
✅ Higher Energy Density – LMFP’s higher voltage profile (~3.9V vs. LFP’s ~3.3V) directly results in 20% higher energy density than LFP.
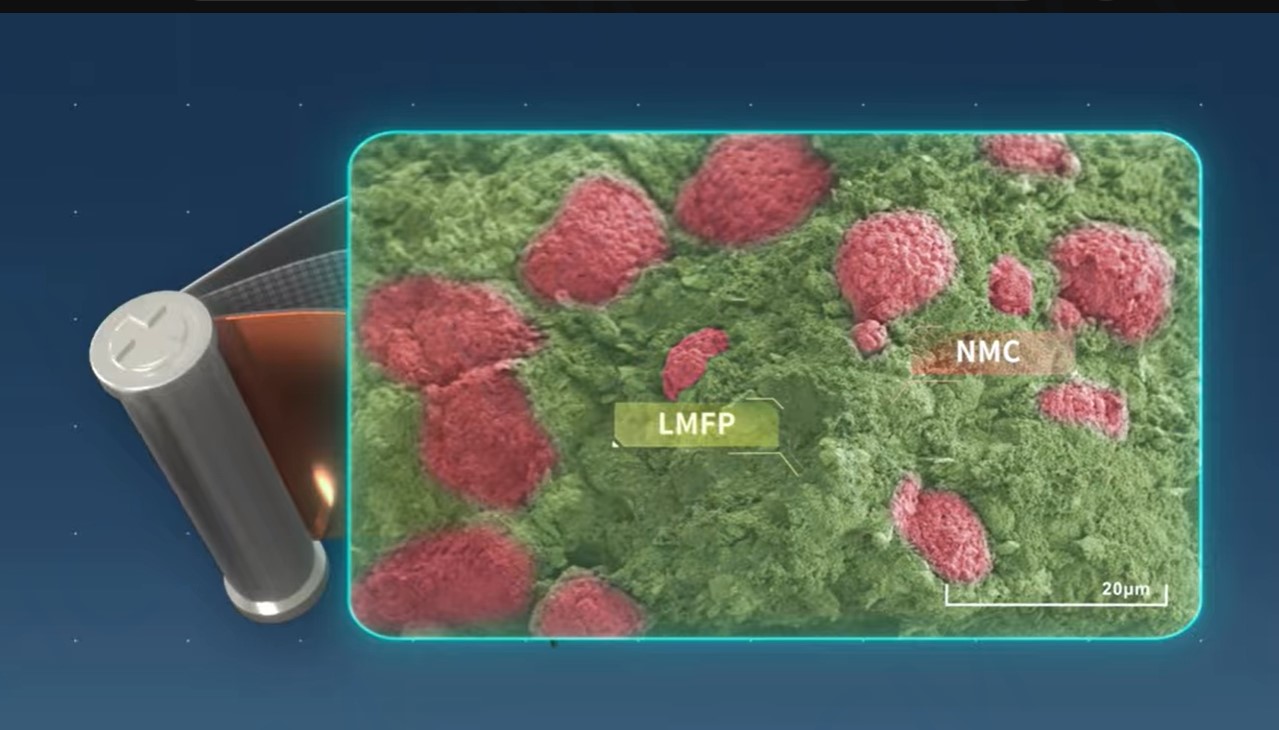
✅ Blending Capability – Unlike LFP, LMFP can be blended with Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) due to their similar discharge voltage windows. This creates more flexible battery systems, allowing for a balance between safety, cycle life, and cost-efficiency.
✅ Strong Safety & Cycle Life – LMFP is also resistant to thermal runaway and offers a long cycle life.
With higher performance and flexible system integration, LMFP could be a game-changer for EVs and energy storage.
Is this the next big leap in battery chemistry? Let’s discuss!